Why metadata is your modern growth lever
Enterprises have mastered collecting data. The hard part now is understanding it at scale, across tools, clouds, and business domains. That is why metadata fabrics are gaining attention, because they create a connective intelligence layer that makes data findable, trustworthy, and ready for AI
Leading references describe data fabrics as architectures that ingest and analyze metadata to recommend integration, organization, and governance actions. A metadata fabric focuses that same power on the metadata itself, turning it into a living asset that guides how data is used, secured, and improved across the enterprise.
What is a metadata fabric in data strategy?
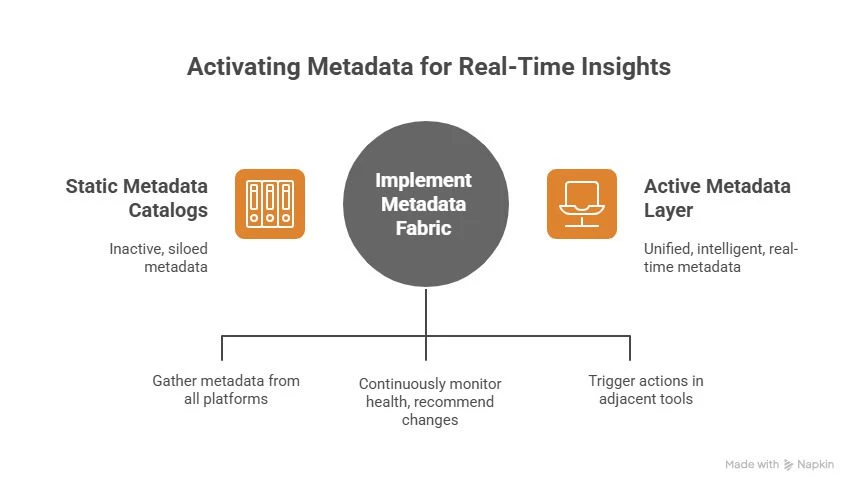
A metadata fabric is a unified, intelligent layer that collects technical, business, and operational metadata from all your platforms, then activates it in real time. Think of it as the orchestration brain for context, lineage, policies, and quality signals that every downstream analytics or AI workflow depends on.
In practice, it builds on the industry’s move from static catalogs to active metadata, where metadata is continuously processed to monitor health, recommend design changes, and even trigger actions in adjacent tools.
Types of Metadata is categorized into three main types:
- Technical Metadata: Defines the structure of data, data types, formats, and schemas, helping engineers ensure proper data system design.
- Operational Metadata: Tracks data processes, lineage, and timestamps, supporting data quality management, auditing, and logging.
- Business Metadata: Adds business context through definitions, ownership, and classification, enabling governance and compliance.
Core principles
- Unified view of metadata across warehouses, lakes, BI tools, pipelines, and SaaS apps.
- Continuous processing that surfaces lineage, usage, and quality as they change.
- Automation hooks that push recommendations or guardrails back into data platforms and catalogs.
- Governance by design through a reusable metadata governance framework.
Metadata fabric architecture, the building blocks
A solid metadata fabric architecture typically includes four layers:
- Connect and collect
Connectors harvest technical metadata from databases and ETL, business metadata from glossaries, and operational metadata from query logs and monitors. Modern data fabric references emphasize that knowledge graphs and active metadata techniques make this practical at enterprise scale. - Unify and model
The platform normalizes metadata into a common model, builds relationships, and maintains a knowledge graph. This enables consistent definitions, impact analysis, and enterprise search across domains. - Activate and automate
AI-powered metadata management evaluates runtime patterns, flags quality or policy issues, and can recommend design changes or automate approvals and routings. Gartner calls this active metadata, which extends beyond documentation to orchestration. - Govern and measure
A metadata governance framework sets ownership, controls, and stewardship workflows. Best practices include standards for naming and definitions, audits, access permissions, and role clarity between data owners, stewards, and platform teams.
Data fabric vs metadata fabric
Both are modern approaches, but they are not the same. A data fabric is an architectural way to connect and deliver data across a distributed landscape. It leverages active metadata and catalogs to route and optimize data access. A metadata fabric concentrates on unifying and activating the metadata layer itself, which then guides governance, discovery, lineage, and AI readiness across any data fabric, data mesh, or hybrid setup. In short, the data fabric moves and serves data
How metadata fabrics improve data governance?
Stronger governance comes from baking policies into the fabric, not bolting them on later. A metadata-driven data strategy uses the fabric to enforce definitions, automate classification, and continuously verify compliance. References on metadata governance emphasize objectives such as making data trustworthy and consistent, aligning with enterprise policies, and preventing unauthorized use. The fabric provides the telemetry and workflows to do this day to day.
Practical wins for governance teams
- Automated PII detection tied to masking or access policies.
- Business glossary terms linked to physical fields, so definitions travel with data.
- Steward queues that open when lineage shows a risky upstream change.
- Audit trails that prove who changed what and when.
Metadata fabric for data lineage and observability
Lineage is the backbone of trust. A metadata fabric consolidates transformation histories, joins them with usage logs, and exposes end-to-end lineage and observability so teams see blast radius, SLA risk, and ownership in one view.
Industry guides note that modern catalogs and fabrics trace lineage, support impact analysis, and use knowledge graphs to map relationships, which the metadata fabric elevates into everyday operational decisions.

AI readiness: Why active metadata matters
AI initiatives require curated, well-understood, and well-governed data. Active metadata gives you the feedback loops to reach that standard, for example, identifying canonical sources, surfacing data contracts, and detecting drift in upstream systems.
Analysts frame active metadata as continuous access and processing that can monitor, evaluate, recommend, and orchestrate in third-party tools. This is precisely the behavior your AI platform needs to stay reliable and cost-efficient.
Benefits of metadata fabric for enterprises
Leaders implement a metadata fabric to reduce cycle time, risk, and cost across the data lifecycle.
- Faster analytics and AI through trustworthy discovery and governed Lower compliance risk via consistent policies and provable lineage.
- Higher developer productivity because impact analysis shortens change management.
- Better platform economics since observability exposes unused assets and redundant pipelines. Industry sources show that modern fabrics and catalogs improve access, standardize meaning, and accelerate safe reuse, which directly translates to value.
Metadata fabric integration with data catalog
Your catalog remains the daily workspace for analysts and stewards. The fabric supercharges it by feeding in relationships, runtime signals, and governance controls. Vendor and analyst materials consistently describe catalogs as central to data fabrics, with active metadata adding real time organization, lineage, and business context. The net result is a metadata fabric platform plus catalog that delivers guided discovery, policy-aware access, and one-click impact analysis across tools.
Implementation playbook, a phased path
- Baseline and scope
Inventory key systems and governance pain points. Start with two or three high-value domains and the most used analytics tools. - Connectors and collection
Prioritize sources that yield the richest metadata, for example, ETL jobs, warehouse query logs, lake catalogs, BI semantic layers, and identity providers. - Model and knowledge graph
Normalize technical, business, and operational metadata. Establish glossary ownership and start mapping terms to physical assets. - Activate high-impact use cases
Choose two automation paths first, such as automated lineage with impact analysis and policy enforcement for sensitive data access. Analyst guidance on active metadata highlights monitoring, recommendations, and orchestration as early value drivers. - Governance operating model
Codify your metadata governance framework, including roles, approval workflows, quality checks, audits, and metrics for adoption. Sources recommend clear standards, periodic reviews, and cross-functional participation from stewards and platform teams. - Measure outcomes and expand
Track time to find data, policy violations prevented, incidents resolved faster due to lineage, and cost savings from retiring redundant assets. Iterate domain by domain.
Frequently asked comparisons
- Data catalog vs metadata management
A catalog is the user interface and library of assets, while metadata management is the broader process of collecting, governing, and activating metadata. You need both, with the fabric as the orchestration layer. - Data fabric vs metadata fabric
A data fabric unifies data access and movement. A metadata fabric unifies and operationalizes metadata so the whole stack becomes observable, governable, and AI-ready. They complement each other.
Key Takeaway
When building a data fabric or mesh, make the metadata layer your priority. A well-structured metadata fabric architecture connects fragmented definitions, logs, and lineage into a trusted control layer for analytics and AI.
The leaders in this space will view metadata as intelligent, reusable assets rather than static documentation. Industry experts and technology providers align on this point: active metadata should be used to observe, guide, and automate improvements across your entire data landscape.
At Prolifics, we help organizations turn this vision into reality. Our experts design and implement intelligent metadata frameworks that unify data across hybrid and multi-cloud environments, enabling better governance, observability, and AI readiness.
With our accelerators, such as automated lineage and governance integrations, we transform metadata from a back-office function into a strategic enabler for decision-making and innovation.




