Data Governance Framework
Data governance is the big picture that understanding data privacy and data management have been building towards. A data governance framework or data governance program explicitly details the organizational steps that each business takes when it comes to overseeing their data. This includes internal policy, data management tasks, external regulatory mandates, and more.
Data governance is complex and individualized for each business; however, there are some static points that it helps to understand. In this section of the guide, we will explain the benefits of a data governance plan, how it relates to data privacy, the key components of a data governance framework, and the problems that a data governance framework seeks to solve.
Related post: Data Governance in Healthcare
The Role of Data Governance in Data Privacy

Data governance is an overarching term that encompasses all of the data management practices implemented by a business. The official definition of data governance published by Gartner is “the specification of decision rights and an accountability framework to ensure the appropriate behavior in the valuation, creation, consumption, and control of data and analytics.”
Another helpful definition comes from Utopia and it is that data governance is the “management of data to validate for accuracy as per the requirements, standards, or rules that an individual organization needs for their individual business.”
In regards to data privacy, data governance is essential. Data governance is essentially a process through which businesses ensure and maintain data privacy. These practices are also designed to make sure that a business has data that adds value to itself, that data is usable, accurate, and secure.
Data governance is also the basic outline that a business can use to make sure that they are in line with all of the regulations that exist and this outline can be adapted as new legislation is created. Having a specific plan for data governance is how a business can maintain and protect data privacy.
Related post: You Really Can’t Get Around It – Data Privacy Is Data Governance
What Are The Benefits of Data Governance?

As you just read, data governance initiatives are primarily designed to make sure that businesses are adhering to all of the privacy regulations that are imposed on them by law. The main benefit of this process is to make sure that your business is compliant; however, there are benefits that go beyond the idea of legal compliance.
Having a strong process for data governance helps improve the quality of the data that a business collects and stores. It does so by helping to ensure that all of the data is accurate and complete, and provides a sense of consistency across all data because it will all fall under the same governance plan.
This high-quality and complete data that you have can then be used more effectively. Properly stored data will be easier to access and apply to the decision-making process, making it easier to create concrete business plans based on the information that you have. Strong data governance plans also help improve financial performance, through this enhanced and informed approach to decision-making and planning.
Data governance also allows a business to maximize another one of its key assets, money. Clearly outlined processes for managing and storing data makes it so fewer resources need to be put into the process; this improves operational efficiency across the board. Also, having a clear plan helps a business see where their money is going when it comes to data storage and management, making it easier to maximize the efficiency of this process.
Finally, data governance plans include additional training that focuses on how data should be handled. This helps to make sure that no data is lost and helps to mitigate the risks of critical data being compromised later on. The increased training that a data governance plan provides will reduce security violations.
Data governance is something that must be specifically tailored to each business and adapted over time to continually improve the way data is handled. These are just a few of the benefits that it can provide. The way that a strong data governance plan can benefit a business is specific to that one business but, it is a guaranteed roadmap to effective data management across the board. This strengthens businesses and strengthens the necessary data privacy for their clients or customers.
The way that a specific business addresses this process depends on the data governance framework that it creates and adheres to.
What Is a Data Governance Framework?
Supporting business outcomes is important for the future of a business and that can be done by effectively handling data and ensuring that it is used in a consistent way. This is the role that a Data Governance Plan or Data Governance Framework fills for a business. Profisee defines the term data governance as “a set of principles and practices that ensure high quality through the complete lifecycle of your data.”
It is widely advised that a data management system alone is not enough. Instead, businesses need an actionable framework that comprises rules, processes, and procedures to ensure that those rules are followed on a continuous basis. Once all of these components are created, they are now all constituents of an effective data governance framework.
How Is A Data Governance Framework Created?
Data governance frameworks, as you have read by now, are unique to every business. It is important for a business to carefully create their own data governance framework so that they can fully capitalize on their greatest asset. The creation of this plan can be summed up in two parts: goals, and questions.
The first part of creating a data governance framework is detailing what the goals of its implementation are. The most prominent goal for most businesses that are seeking to create a data governance framework is to align themselves with the regulatory requirements set forth by law. With that said, there are other goals that this framework can help them meet, such as data-driven decision making, improved data security, or increasing profits through monetizing data.
The next part of designing a Data Governance Framework involves determining what questions this framework can answer for the business. These questions are the basis for the main components of the framework itself.
A proper Data Governance Framework will help a business clearly understand the types of data it holds and the value of that data. This also includes understanding what a business stands to lose by failing to protect that data.
It will also help businesses determine if all of the data that they have is accurate and that all the details are correct. It also identifies how long that data is believed to be accurate before becoming obsolete.
The biggest question that a Data Governance Framework addresses is whether or not the data is secure. The security of the data is paramount to guaranteeing data privacy. This part of the framework covers software and hardware protections, data access, authentication processes, and more. This question provides insight into the very infrastructure of the business as a whole and applies that insight to data privacy measures.
The security of the data works directly alongside compliance. Data Governance Frameworks can detail the legal obligations that a business faces in regards to how it collects and stores data. Any legal restrictions on the use or release of that data are also addressed by this.
The availability of data is also answered by a Data Governance Framework. This part of the framework explores the way that data is stored, how it is secured through backups, and the overall process of system recovery if anything bad should happen that results in data loss.
Finally, it also dictates the level of authorization, responsibility, and involvement that each employee will have within the framework.
Data Governance Frameworks touch every area of a business because they help keep track of all data assets. Other important factors of data management are also covered by the framework such as determining the sensitivity of data, keeping data organized and easy to integrate, properly classifying data for the purpose of long term storage and eventual purging, and more.
Each of these things are important components of a Data Governance Framework; however, there are no set rules on what a framework must be. Instead, these are just guidelines for components to include.
What Are The Key Components of a Data Governance Framework?
According to The Data Governance Institute, a Data Governance Framework is “a logical structure for classifying, organizing, and communicating complex activities involved in making decisions about and taking action on enterprise data.”
While that is a very complex explanation, there is one main thing to understand about how Data Governance Frameworks actually work. The three overall components or “branches” of the framework are people, processes, and technology. In any Data Governance Framework, it works because people execute the framework through processes that are supported by technology.
Below those overarching components lie the framework itself, which consists of multiple smaller components. These are the pillars that support the framework or, perhaps more accurately, the skeleton of the complex body of data governance for a company. A great way to think about these concepts is that they are the things that the framework must address in order to be complete.
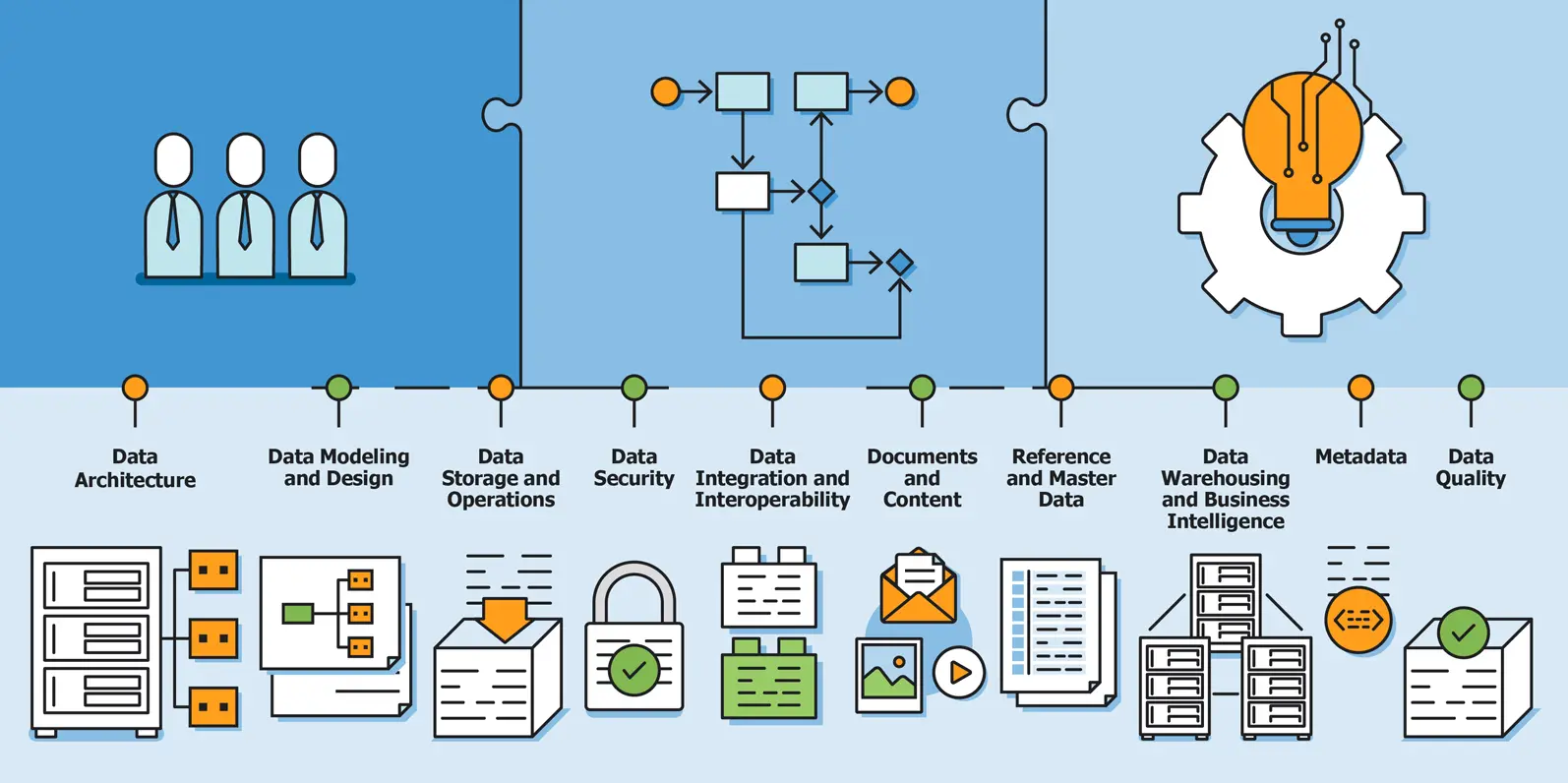
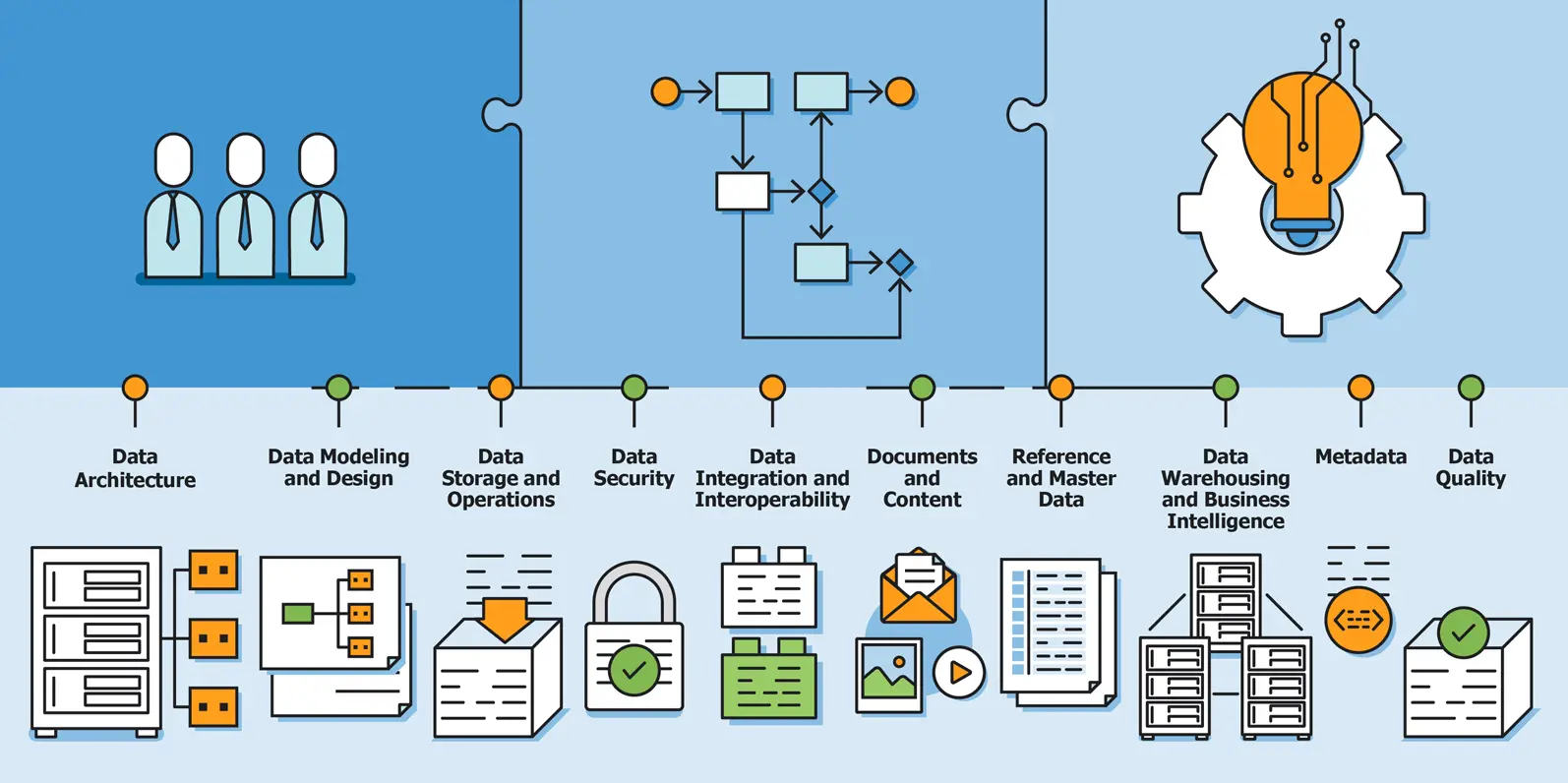
There are a plethora of examples when it comes to how a Data Governance Framework should be constructed in order to best serve a particular business. However, The Data Management Association International has outlined the following areas of data management knowledge as key components of a strong Data Governance Framework.
Data Architecture
A Data Governance Framework should clearly outline the way that data will be structured. This includes the data itself and all data-related resources. This area of the framework will include all of the policies that determine the steps in the Data Lifecycle Management process for a business. This will address what data will be collected, how it will be organized and stored, and more. Another key part of data architecture is determining how data will be integrated and analyzed in order for that data to be useful.
Data Modeling and Design
According to Dataversity, the term data modeling refers to “the practice of documenting software and business system design.” A great way to think about data modeling is that it is the outline that the data architecture will follow. In a Data Governance Framework, information about data models should be included because this framework is designed to be a complete resource of data management within a business. This portion of the framework should detail how data models will be designed, built, tested, and maintained to guarantee that the data architecture is accurate and functional while providing the most benefit to a business.
Data Storage and Operations
Data is going to be stored or archived throughout the duration of its life cycle and this element of a Data Governance Framework is what will create the guidelines that support the overall database for a particular business. These guidelines address how data storage systems will be designed, the way that data will be organized within that storage, and how the system will be implemented. This is another element of the framework that exists to support the overall data architecture that you’ve created.
This part of the framework should also address the processes for backing up the data that is stored and how it will eventually be purged at the conclusion of its life cycle.
Data Security
Data security is another key component of a Data Governance Framework. Data security refers to how all digital data will be protected once it has been collected. This part of the framework will outline the process for protecting that data from unauthorized access, data breaches, cyber-attacks, theft, and more. In addition to that process, this area of the framework should also address who is given access to certain data sets, and the procedure for responding to any destructive force.
The data security component of the overall framework will ideally have fully articulated data protection policies and specific action steps to take after something like a data breach or unauthorized access or use of the data.
Data Integration and Interoperability
Businesses collect data from a variety of sources, typically. In this area of a Data Governance Framework, the process for making sure that all data is unified and properly organized should be addressed. This includes the way that all data from any source can be integrated with other data sets and will describe the process for making sure that all of the available data can be used together whether that is for informing decisions, analyzing operations, and so on. Consolidating data effectively serves two purposes. The most important problem that data integration seeks to solve is making sure that all data is properly handled to maintain data privacy and ensure data viability.
Secondly, data integration ensures the interoperability of all of the data a business collects, which is the most effective way that a business can gain thorough insights based on all of the information, which allows them to use data to better support operations.
Documents and Content
Documents and content fall into the category of unstructured data. Structured data is what most of the previous components deal with. Structured data is any data set that is clearly defined and organized. Good examples of structured data could include the names or billing information for a group of customers, for instance. Unstructured data is everything else.
Unstructured data includes things like images, emails, documents, and so on. In a good Data Governance Framework, there will be procedures for handling unstructured data. This type of data has to be indexed differently, stored differently, and will require a separate process for protecting it. Because unstructured data is different, a Data Governance Framework that is effectively designed will address the way this type of data is handled and provide clear avenues for making that data available for integration with the existing structured data sets.
Reference and Master Data
Master data is the most critical data for the operation of a particular business. According to Semarchy, there are five categories of master data. These are:
- Financial and Organizational
- Parties
- Places
- Things
- Reference Data
Master data will include the lists of everyone that conducts business with a particular business, what the business sells or manages, accounting information, and so much more. Within a Data Governance Framework, there need to be protocols created for this data to ensure that it is easily accessible to all relevant parties within an enterprise. This component of the framework will also standardize the definitions of master data and create a single source for this data to reduce redundancy and errors that pertain to this category of information.
Having high-quality master data and effective systems for managing that data are critical to the operations of any business.
Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence
A data warehouse is sometimes referred to as an enterprise data warehouse; it is defined as “a technology that aggregates structured data from one or more sources so that it can be compared and analyzed for greater business intelligence,” according to Informatica.
This component of a Data Governance Framework should include the process for managing all of this key analytical data. Data warehousing is designed to provide a larger view of the data over a longer period of time so that it can be used to inform business decisions; in light of that, this part of an effective framework needs to address how this data can be accessed and how it will be maintained over time.
This component of the framework will also include all of the necessary information about the software and supporting tools that will be used when it comes to this data and the methodology for applying that data to the enterprise.
Metadata
According to TechTarget, metadata is “data that describes other data.” This type of data includes information about the sources of other data, the date that it was collected or created, the size, and when it was last updated.
This type of information is important to a business because it helps create accountability in the chain of access to that data. If something was entered incorrectly or handled improperly, the metadata can pinpoint where those problems occurred. It also helps improve the overall organization and classification of data and can support all of the processes in Data Lifecycle Management.
In a Data Governance Framework, how this data will be collected, organized, managed, and integrated with other relevant data sets should be outlined.
Data Quality
The final component in a Data Governance Framework should address data quality. This portion of the framework should explicitly define the standards of quality for the existing data as well as provide guidelines for managing that data over time to ensure that it maintains its integrity.
This should also include a process for monitoring data, keeping it up to date, and lay out a plan of action for improving data quality on a continuous basis. High-quality data is necessary for a business because data storage and management is an expensive process; maintaining efficiency and ensuring that all data has value is of the utmost importance. These are the types of things that should be handled within this element of a Data Governance Framework.